Materials & Technologies
Our ambition is to use more sustainable materials and, through gradual improvement in quality, ensure a longer lifespan for our products. We only use PFC-free water repellent impregnations, and we are consistently working to increase our use of recycled materials. We are constantly developing new ways to become better, more transparent, and fair at all levels. We have embarked on our journey towards a more sustainable collection and continue to push the issue forward, to further develop our materials and requirements.
The Pinewood InsectSafe® technology revolutionizes the way of protecting outdoor clothing against insects. Lightweight, breathable, and built for adventure, our InsectSafe® clothing is designed for warm climates where function matters most.

BIONIC-FINISH® ECO
For several years now, we have chosen to switch to fluorocarbon-free impregnation for all our fabrics. Fluorocarbons are difficult to manage and take a long time for nature to break down. Fluorocarbons have also been shown to affect the immune system, be endocrine disruptors, and are suspected to be carcinogenic in humans and other mammals. We have opted to work with Bionic-finish Eco - a more environmentally friendly and fluorocarbon-free (PFC) water and dirt repellent treatment that helps keep the outer fabric of functional garments dry. The treatment ensures that the garment retains its breathability and original weight, whether it is with or without a membran
Pure Waste®
In our "Save Water" series, we use recycled fabric from Pure Waste®. The production process for this material uses 99% less water and has 50% lower carbon emissions compared to production processes of similar products. The products are made from 100% recycled material, consisting of leftover fabric scraps, 60% recycled cotton, and 40% recycled polyester, within the textile industry. The leftover fabric is sorted by colour, broken down into fibre, and spun into new yarn. This process allows for the production of fabrics without new dyeing and without the use of fresh cotton. The fabric is transformed into products whose production process saves large amounts of water.
For more information visit www.impactreport.app/purewaste/
Polyester
Polyester is an extremely durable synthetic fibre used in textiles, clothing, and hook-and-loop fasteners. It is ideal for manufacturing outdoor clothing as the material has low water absorption, is durable, and is comfortable to wear. Other excellent properties of polyester include colour retention and its ability to stay smooth and neat. Since its production began in the 1950s, polyester has become the world's second most important textile fibre, after cotton, accounting for 30% of global textile usage. Polyester is a synthetic, oil-based material made by melting granulate flakes into a liquid mass. It is then blown out through a nozzle (similar to a shower head) to form its long fibres. Once the fibres have dried, they are spun into threads and woven into fabric.
Recycled Polyester
To minimize our environmental impact when using polyester, we utilize as much recycled polyester as possible. By using polyester primarily from recycled PET bottles, we can reduce resource use and energy consumption by about 70%. The result is a very strong and durable material that is ideal for outdoor clothing.

Cotton
Cotton has been used for textile manufacturing for thousands of years and is the most produced fabric fibre in the world. It is a natural seed fibre that grows on bushes and is a relatively difficult crop to cultivate as it is sensitive to weather, insects and diseases. To grow one kilo of cotton fibres, it takes about 10,000 litres of water, which requires an irrigation system. Cotton fibre has good durability and becomes stronger when wet, meaning it doesn't need to be handled too delicately during washing. Cotton is also hypoallergenic, making it less likely to cause allergic reactions.
Organic cotton
Organic cotton is a natural fibre that is biodegradable and renewable, making it gentle on the environment. With a good balance of different plants, natural fertilizers, and cotton bushes, the cotton can be grown without the use of toxic and persistent pesticides as well as synthetic fertilizers. By creating a favourable environment for the natural enemies of pests in this way, attacks on the plants are reduced. Fewer chemicals mean a lower risk of allergies and skin irritations for the wearer. Organic cotton is also soft on the skin and promotes air circulation, making it comfortable to wear. At Pinewood, we use certified organic cotton.
Recycled cotton
Recycled cotton is a natural fibre whose production reduces the use of natural resources as well as the consumption of water and chemicals. Recycled cotton textiles are made from pre- and post-consumer waste, and use a smaller amount of virgin cotton. This contributes to reducing the negative environmental impacts associated with cotton cultivation, such as high water consumption, carbon emissions, intensive land use, and transforms textile waste into new products. Recycled cotton is a soft and airy fibre. It is biodegradable and renewable, and contributes to reduced use of natural resources, water, and chemicals, which is crucial for sustainable textile production.

Wool
Wool is a natural fibre that is both renewable and biodegradable, reducing environmental impact. It efficiently retains heat, making it ideal for colder climates, and is self-cleaning as the unique properties of wool fibres contribute to less need for frequent washing. It is also water resistant and offers natural protection against moisture without becoming soaked through. Wool material allows the skin to breathe, enhancing comfort. We only use mulesing-free wool. Mulesing is a procedure that involves scalping the rear part of a sheep, often performed without anesthesia, which is highly traumatic and painful for the animal.
Hemp
Hemp is a natural fibre that is strong, durable, and quick-drying, making it ideal for outdoor clothing that requires a long lifespan. The hemp plant is naturally resistant to pests, fungi, and diseases, which reduces the need for herbicides and pesticides. During cultivation, it requires minimal water and no fertilizers. Therefore, hemp has a lower carbon footprint compared to virgin polyester, for instance.
Biosynthetic materials
Biosynthetic materials represent a sustainable alternative to traditional fibres. Ultramid® Biomass Balance Polyamide is an artificial and renewable fibre made from 100% bio-based nylon fabric derived from castor oil and organic waste. The production of bio-based fibres requires no fossil fuels. Biosynthetic materials have a significantly lower carbon footprint compared to conventional polyamide, as they produce three times less greenhouse emissions.
Recycled polyamide
Recycled polyamide is an artificial fibre made from recycled materials, including pre- and post-consumer waste. Post-consumer waste often includes used and discarded products as well as collected fishing nets from the oceans. Advantages of the material are that it is strong, durable, and quick-drying, and emits a lower carbon footprint than newly produced polyamide.
Linen
Linen is a type of natural bast fibre known for being fast-growing and easy to cultivate. During its cultivation, linen requires very few chemical treatments. It is biodegradable and renewable, which reduces its environmental impact. Cultivation of linen requires fewer resources and less time to grow, which is advantageous for sustainable production. Linen is a sustainable, breathable, degradable, and renewable fibre that contributes to high comfort and suitability for clothing.
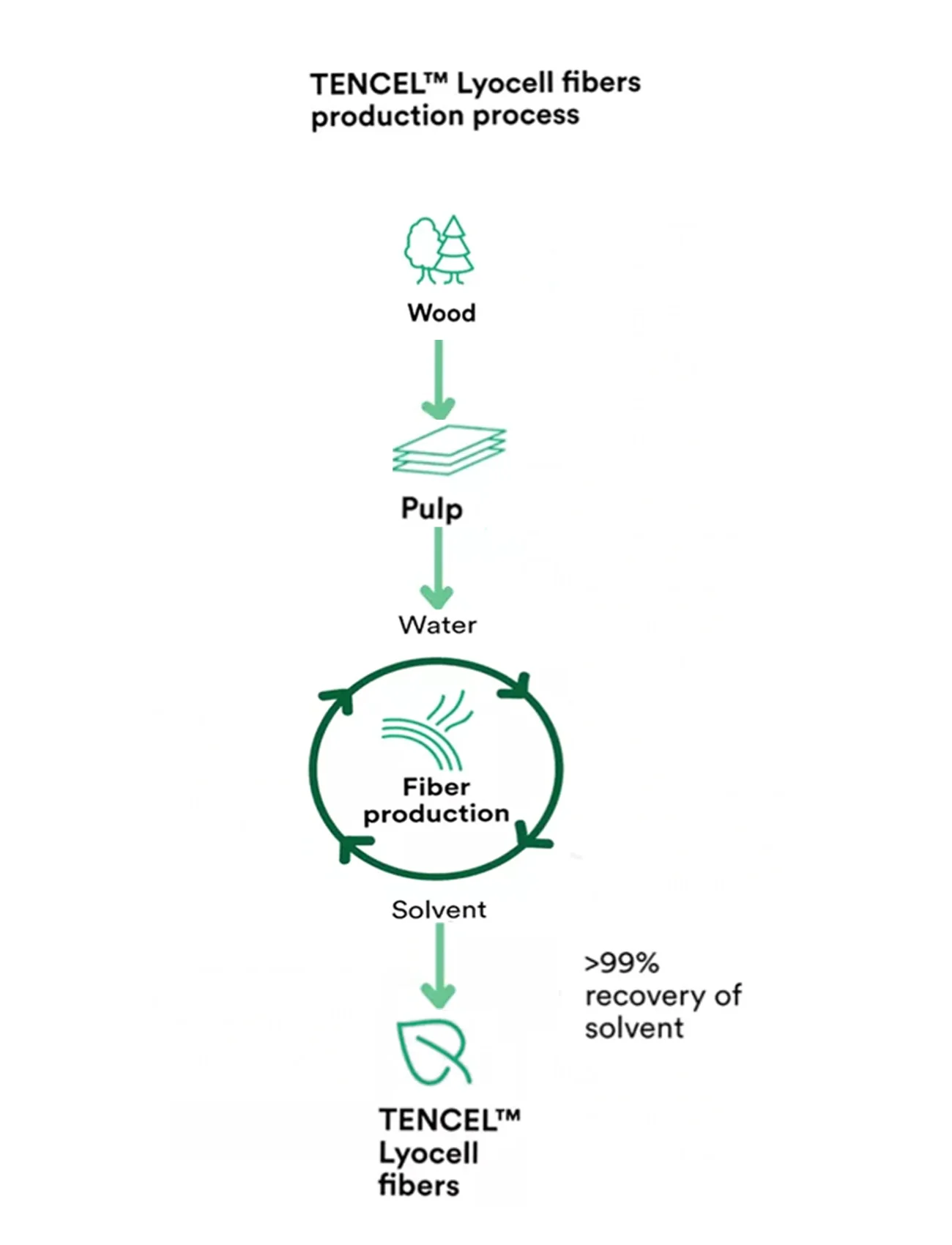
TENCEL™
TENCEL™ is a sustainable natural material that is more gentle on the environment than cotton and viscose, and also has superior features. TENCEL™ is produced from natural forests or sustainable forest plantations. It is renowned for its environmentally friendly manufacturing process, which recycles water and reuses the solvent at a recovery rate of 99%. Compared to conventional lyocell, viscose, and cotton, TENCEL™ has the lowest environmental impact, six times lower than cotton. It is a temperature-regulating material that actively reduces body temperature. TENCEL™ fibres have high breathability and make the fabric 20% cooler than, for example, wool. The fibres also have high moisture absorption capacity, the same level as wool but with a softer and less prickly surface. TENCEL™ is also minimally static. Unlike cotton, polyester, and synthetic materials, TENCEL™ constitutes an unwelcome environment for bacteria. The fabric contains nanofibrils that act as a network of channels leading moisture away from the surface. The fibres' ability to absorb moisture means that bacteria find it difficult to grow on the fabric as the fibre surface remains dry during higher activity or humidity. Studies have shown that TENCEL™ fibres reduce odour formation. The fabric was tested with armpit patches during both indoor and outdoor training, and the difference was noticeable.
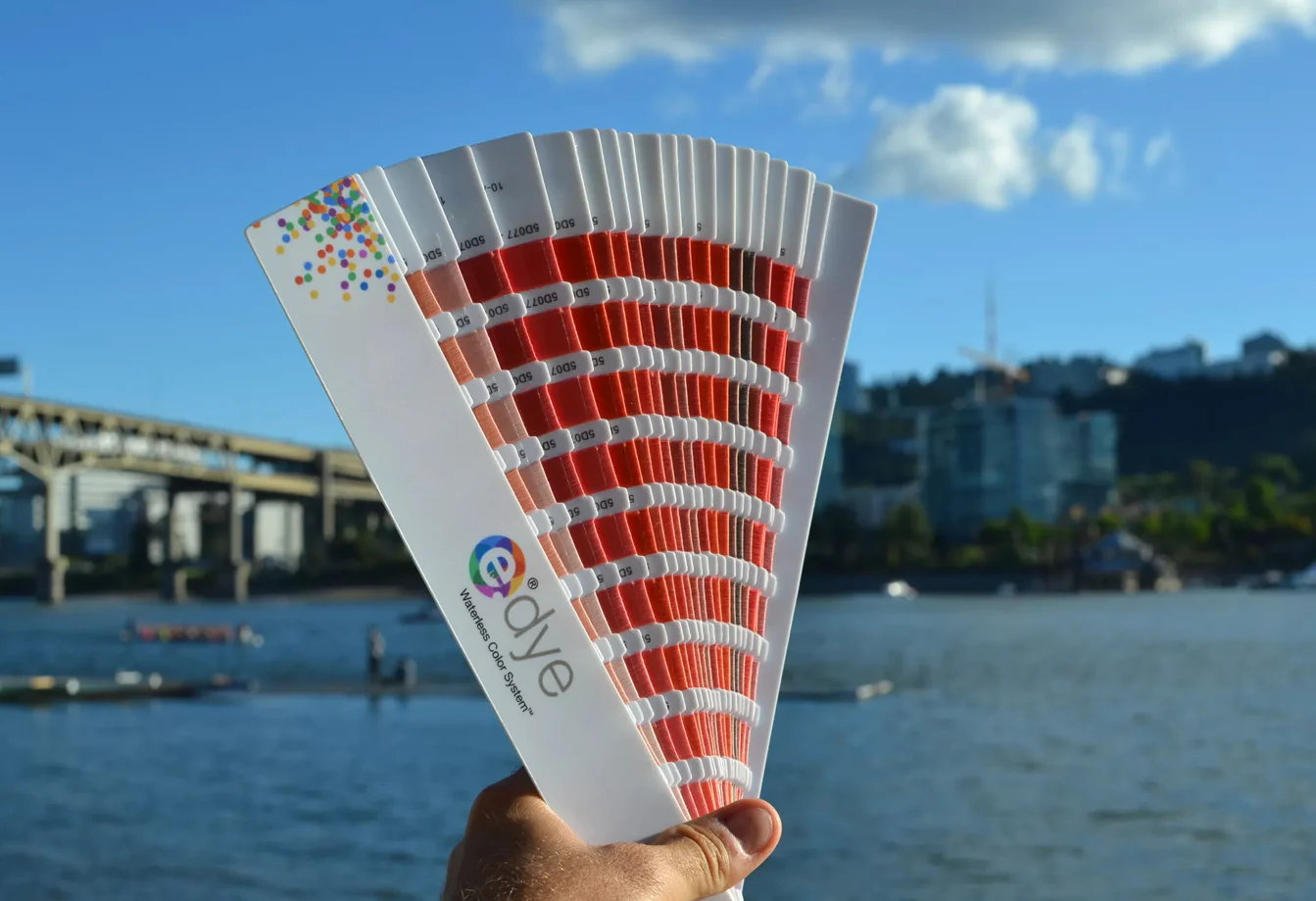

e.dye®
e.dye® is an eco-friendly system for dyeing textiles. It is a waterless dyeing system where the colour is integrated directly into the fibres before they are spun into yarn. Conventional dyeing processes use 22 litres of water to dye 2 metres of fabric, while e.dye® does not use not a single drop. In addition to water savings, the e.dye® process requires less energy consumption, reduces CO2 emissions, and uses fewer chemicals compared to traditional processes. Unlike traditional water-based dyeing processes, e.dye® colour is permanent. This means that the colours do not fade or bleed onto adjacent colours during washing. In addition to significant water savings, e.dye® products have a superior finish and a broader colour range with over 5000 colours. The colours have been developed using mathematically derived pigment and colour formulas. This allows e.dye® to recreate the exact same colour over and over again, from prototype to bulk production. The colour you see in the sample is the same as you will see in the fabric. This is not the case of any other conventional dyeing system where the risk of colour variation is greater.